How To Use SVM In Python?
What is SVM?
Intuitively, a good separation is achieved by the hyperplane that has the largest distance to the nearest training-data point of any class (so-called functional margin), since in general the larger the margin the lower the generalization error of the classifier 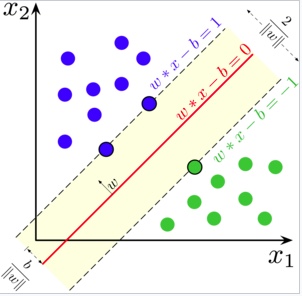 SVM
SVM
Soft-margin
Gradient
What’s the gradient of multiple class gradient?
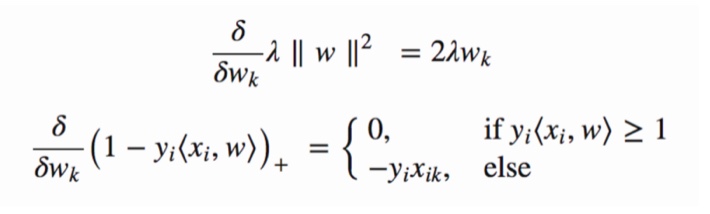 SVM_principle
SVM_principle
and when not correct
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import numpy as np
df = pd.read_csv('iris.csv',index_col = False, delimiter = ',')
df = df.drop(df.index[list(range(100,150))]) # to binary classification
df = df.drop(['SepalWidth','PetalWidth'],axis= 1)
df['Species'] = np.where(df['Species']==0, -1, 1)
Y = df['Species']
X = df.drop(['Species'],axis=1)
X, Y = shuffle(X,Y)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, train_size=0.8)
x_train = np.array(x_train)
y_train = np.array(y_train)
x_test = np.array(x_test)
y_test = np.array(y_test)
y_train = y_train.reshape(len(x_train),1)
y_test = y_test.reshape(len(x_test),1)
train_f1 = x_train[:,0]
train_f2 = x_train[:,1]
train_f1 = train_f1.reshape(len(x_train),1)
train_f2 = train_f2.reshape(len(x_train),1)
w1 = np.zeros((len(x_train),1))
w2 = np.zeros((len(x_train),1))
epochs = 1
alpha = 0.0001
W = np.zeros((len(x_train),2))
while(epochs < 10000):
y = w1 * train_f1 + w2 * train_f2
prod = y * y_train
print(epochs)
count = 0
for val in prod:
if(val >= 1):
cost = 0
w1 = w1 - alpha * (2 * 1/epochs * w1)
w2 = w2 - alpha * (2 * 1/epochs * w2)
else:
cost = 1 - val
w1 = w1 + alpha * (train_f1[count] * y_train[count] - 2 * 1/epochs * w1)
w2 = w2 + alpha * (train_f2[count] * y_train[count] - 2 * 1/epochs * w2)
count += 1
epochs += 1
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
## Clip the weights
index = list(range(len(x_test),len(x_train)))
w1 = np.delete(w1,index)
w2 = np.delete(w2,index)
w1 = w1.reshape(len(x_test),1)
w2 = w2.reshape(len(x_test),1)
## Extract the test data features
test_f1 = x_test[:,0]
test_f2 = x_test[:,1]
test_f1 = test_f1.reshape(len(x_test),1)
test_f2 = test_f2.reshape(len(x_test),1)
## Predict
y_pred = w1 * test_f1 + w2 * test_f2
predictions = []
for val in y_pred:
if(val > 1):
predictions.append(1)
else:
predictions.append(-1)
print(accuracy_score(y_test,predictions))
## Output
or
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
clf = SVC(kernel='linear')
clf.fit(x_train,y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
print(accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred))
Welcome to share or comment on this post: